- List of Acronyms
- Glossary of Terms
- Executive Summary
- Introduction
- Background
- Governance
- Information Management and Retention
- Training and Resourcing
- Case Study: [**redacted**]
- Conclusion
- ANNEX A: Technical considerations in the lifecycle of Canadian and foreign datasets
- ANNEX B: Briefings & Interviews
- ANNEX C: Findings & Recommendations
Date of Publishing:
List of Acronyms
| ACRONYM | Description |
|---|---|
| CSIS | Canadian Security Intelligence Service |
| DAG | Data Acquisition and Governance |
| DDO | Deputy Director of Operations |
| DMEX | Data Management and Exploitation |
| ERC | External Review and Compliance |
| FC | Federal Court |
| IC | Intelligence Commissioner |
| JA | Judicial Authorization |
| NSA 2017 | National Security Act 2017 |
| NSIRA | National Security and Intelligence Review Agency |
| ODAC | Operational Data Analysis Center |
| PAD | Publicly Available Dataset |
| PCO | Privy Council Office |
| PS | Public Safety Canada |
| SIRC | Security Intelligence Review Committee |
Glossary of Terms
Approved classes of Canadian datasets. Categories of Canadian datasets approved by the Minister and authorized by the Intelligence Commissioner. The Canadian Security Intelligence Service can only collect and retain a Canadian dataset if it falls under an approved class.
Canadian dataset. A dataset that predominantly relates to individuals within Canada or Canadians.
Dataset. A collection of information stored as an electronic record and characterized by a common subject matter.
Designated employee. An employee designated by the Minister who can carry out one or more activities referred to in sections 11.07 and 11.22, such as evaluating, querying, and exploiting section 11.05 datasets.
Dataset regime. Sections 11.01 to 11.25, 27.1 of the Canadian Security Intelligence Service Act governing datasets.
Evaluation. The period in which designated employees shall, as soon as feasible but no later than the 90th day after the day on which the dataset was collected, evaluate the dataset and confirm if it:
- Was publicly available at the time of collection;
- Predominantly relates to individuals within Canada or Canadians and whether it belongs to an approved class; or
- Predominantly relates to individuals who are not Canadians and who are outside Canada or corporations that were not incorporated or continued under the laws of Canada and whoa re outside Canada
Exigent circumstances. A situation in which there is a danger to the life or safety of an individual or a situation requiring the acquisition of intelligence of significant importance to national security, the value of which would be diminished or lost if the Canadian Security Intelligence Service is required to comply with the authorization process under section 11.13 or sections 11.17 and 11.18.
Exploitation. A computational analysis of one or more datasets for obtaining intelligence that would not otherwise be apparent.
Foreign dataset. A dataset that predominantly relates to individuals who are not Canadians and who are outside Canada or corporations that were not incorporated or continued under the laws of Canada and who are outside Canada.
Judicial Authorization. The process by which a Federal Court judge authorizes the retention of a Canadian dataset.
Minister. In this report, Minister refers to the Minister of Public Safety.
Publicly available dataset. A dataset that was publicly available at the time of collection.
Query. A specific search, with respect to a person or entity, of one or more datasets, for obtaining intelligence.
Section 12 investigations. Investigations carried out by the Canadian Security Intelligence Service that relates to threats to the security of Canada.
Threat to the security of Canada. Activities within or that relate to Canada that involve the following:
- Espionage or sabotage;
- Foreign influenced activities;
- The threat or use of acts of serious violence against persons or property for achieving a political, religious, or ideological objective; and
- Activities directed toward undermining by covert unlawful acts, or directed toward or intended ultimately to lead to the destruction or overthrow by violence of, the constitutionally established system of government in Canada.
Executive Summary
The Government of Canada introduced the dataset regime through the National Security Act 2017 (NSA 2017) as a modification to the CSIS Act in July 2019. This regime, constituting sections 11.01-11.25 of the Canadian Security Intelligence Service Act (CSIS Act, hereafter the Act), enables CSIS to collect and retain datasets containing personal information that are not directly and immediately related to activities that constitute a threat to the security of Canada, but are likely to assist in national security investigations.
This review has four sections. The first section, the governance section, describes how CSIS has implemented the regime, CSIS’s first judicial authorization for a Canadian dataset, legislative gaps in the Act, and the department’s internal policies governing the regime. The second section of this review concerns CSIS’s dataset information management and retention practices. The third section concerns how CSIS trains its employees on their dataset regime-related duties and obligations as well as resourcing challenges. Finally, this review includes a case study that encompasses the issues and obstacles related to all of the above-mentioned sections.
In terms of governance and implementation, the National Security and Intelligence Review Agency (NSIRA) found that CSIS’s current application of the dataset regime is inconsistent with the statutory framework. CSIS’s current approach to dataset information collection under section 12 risks the creation of a parallel collection mechanism, one that weakens s.12’s statutory thresholds and simultaneously lacks the external oversight regime intended to protect personal information under the dataset regime.
In 2021, CSIS sought judicial authorization to retain the first Canadian dataset, but in a manner that leads NSIRA to doubt the Federal Court was fully apprised of the internal contradicting views concerning the datasets use prior to the invocation of the dataset regime. Moreover, pending the judicial authorization, CSIS conducted queries pursuant to the exigent circumstances authorization, and retained partial name matches. NSIRA found that the results retained thereof did not meet the strictly necessary threshold applicable for the retention of this information pursuant to section 12 of the Act. NSIRA recommends that CSIS immediately destroy any record containing the names retained pursuant to the exigent circumstances queries, as they do not meet the “strictly necessary” threshold.
This review highlights a gap in the CSIS Act that presents issues as to the governance of foreign datasets. NSIRA notes that the current Act does not provide a time limitation for the Minister, or the Minister’s designate, to authorize the retention of a foreign dataset. Prior to the dataset regime, CSIS collected bulk data that would no longer be compliant pursuant to the new regime. After the dataset regime came into force, CSIS submitted on October 11, 2019, several foreign datasets to the Director, acting as the Minister’s designate. The Intelligence Commissioner (IC) approved the first foreign dataset from this bulk data on December 16, 2020. As of December 2022, CSIS had only submitted two more requests for approval to the IC, totalling three approvals in three years. NSIRA notes that the legislative gap allows the authorization request to remain before the Director, un-actioned for years, and puts into question how CSIS will meet the “likely to assist” threshold and utility of these datasets. NSIRA recommends adding a time limitation for the authorization of a foreign dataset by the Minister or the Minister’s designate.
The final piece on the governance section of this review focuses on the policies CSIS adopted for the dataset regime. NSIRA found that CSIS policies governing publicly available datasets do not contain a requirement for a reasonable expectation of privacy analysis of the collected information. This issue is especially pertinent when considering the strong emerging market for data purchased through data brokers and risks associated with purchasing commercially available information that collectors may have unlawfully collected. NSIRA recommends that CSIS meaningfully analyze and document any possible reasonable expectation of privacy when evaluating publicly available datasets. NSIRA also found that CSIS does not have a policy governing transitory information and that the existing internal directive does not provide employees with sufficient instruction which may result in CSIS retaining information that would otherwise be subject to the dataset regime.
This review’s second section concerns information management and retention of section 11 datasets. From 2018-2019, CSIS conducted an inventory of its holdings to identify information that would be subject to the dataset regime once it came into force. In early 2022, CSIS identified multiple incidents of data, operational reports, and Canadian information extracted from foreign datasets that should have been destroyed. Having identified the non-compliance, CSIS proceeded to implement remedial actions to ensure that any such data is identified and destroyed. In October 2022, NSIRA conducted a search in CSIS’s corporate system and found files containing tens of thousands of entries of Canadian personal information extracted from foreign datasets as well as information amounting to foreign datasets. NSIRA was not provided a satisfactory explanation as to why this information continues to be retained in CSIS’s corporate system or how CSIS distinguishes this information from what it had previously identified as a non-compliance. NSIRA finds that, as of August 2023, CSIS did not comply with the dataset provisions in the CSIS Act because it retained Canadian information extracted from foreign datasets, and foreign information amounting to a dataset.
Moreover, NSIRA did another search in CSIS’s operational repository and found information that would amount to a Canadian dataset. CSIS had not sequestered the operational report, rendering it accessible to all who use the system, contrary to the dataset regime’s retention obligations. NSIRA informed CSIS of this report and was informed it would be treated as a compliance incident. NSIRA again conducted a second search and found another report containing information that would otherwise amount to a Canadian dataset. NSIRA finds that CSIS did not comply with the dataset provisions of the CSIS Act because it retained Canadian information and referenced it as recently as 2022. NSIRA recommends that CSIS immediately destroy Canadian and foreign information found in its corporate and operational repositories that is not strictly necessary to retain. This non-compliant information no longer falls within the legal 90-day evaluation period and retaining it pursuant to the dataset regime is no longer a possibility. NSIRA recommends that CSIS cease to create duplicates of information reported in the operational system and conduct an exhaustive scan of its operational and corporate repositories to identify any non- compliant information.
This review’s third section focuses on training and resourcing. Prior to the coming into force of the dataset regime, CSIS developed and implemented training for the designation of employees pursuant to the dataset regime and mandatory training for all operational employees. NSIRA finds that the training required to become a designated employee to evaluate, query, and exploit section 11 datasets offers clear information on collection and retention requirements. However, NSIRA finds that CSIS operational personnel, including those predominantly dealing with bulk information collection, have not received adequate training allowing them to identify when collected information may fall within the dataset regime. The training is offered on a once-and-done basis for operational employees and contradicts CSIS’s current application of the regime. NSIRA recommends that CSIS develop and deliver scenario-based workshops to train operational personnel on CSIS’s current application of the dataset regime so that they can engage subject matter experts as necessary.
Encompassing all the above-mentioned issues, NSIRA identified a case study that illustrates the challenges CSIS faces in its implementation of the dataset regime. The case involved a dataset containing information regarding thousands of Canadians. NSIRA finds CSIS collected information in relation to activities that could not on reasonable grounds be suspected to have constituted a threat to the security of Canada and the collection, analysis and retention of which was not strictly necessary. The Department of Justice and CSIS managers did not present CSIS executives the totality of information regarding the dataset at the point of collection. The information was also collected absent an analysis of the Charter and privacy considerations. NSIRA recommends that CSIS immediately destroy the case study dataset it collected pursuant to section 12. This information no longer falls within the legal 90-day evaluation period and retaining it pursuant to the dataset regime is no longer a possibility.
The review concludes that CSIS has failed to adequately operationalize the dataset regime. CSIS did not seek to clarify legal ambiguities [**redacted**] of the application of the regime before the Court when given the opportunity to do so. Rather, CSIS has adopted multiple positions on the application of the dataset regime, and now risk limiting what is a collection and retention regime to a retention mechanism. Internally, CSIS has not provided sufficient resources and training to ensure compliance with the regime. Absent an internal commitment to adequately operationalize, resource and support the implementation of a new legal regime, any such regime will fail no matter how fit for purpose it is perceived.
Introduction
Authority
The National Security Intelligence Review Agency (NSIRA) conducted this review pursuant to 8(1)(a) of the National Security Intelligence Review Agency Act.
Scope of the review
NSIRA reviewed the Canadian Security Intelligence Service’s (CSIS, or the Service) implementation of the dataset regime between January, 2019 and June 30, 2022. As the review progressed, NSIRA found it necessary to also consider pertinent information outside of this scope.
Methodology
NSIRA conducted document reviews, interviews, and received briefings. NSIRA also received onsite demonstrations of systems by CSIS subject matter experts. Direct access to these systems was also granted to NSIRA.
Review statements
NSIRA was able to verify the information it received during the review in a manner that met its internal expectations and requirements. NSIRA had direct access to CSIS systems and repositories, and therefore was able to corroborate information.
With respect to responsiveness, while there were minor instances where CSIS did not provide the totality of the information to NSIRA, overall CSIS met NSIRA’s expectations for responsiveness.
Background
In 2015, the Security Intelligence Review Committee (SIRC), NSIRA’s predecessor, reviewed the collection and retention of information related to CSIS’s Data Acquisition Program. The review examined CSIS’s bulk datasets regime and noted that “SIRC has seen no evidence to suggest that CSIS has systematically taken the CSIS Act s 12 statutory threshold of ‘strictly necessary’ into consideration; CSIS’s lack of process, governance and legal guidance around the acquisition and management of bulk data is lacking and non consistent with the practice of close allies.”
Following the publication of SIRC’s annual report, the Federal Court (hereafter the Court) considered data retention issues in the 2016 “Associated Data” decision. The Court found that CSIS had exceeded the limitations of its legislative mandate by retaining information contrary to the “strictly necessary” limitations prescribed by section 12(1) of the Canadian Security Intelligence Service Act (CSIS Act). Under the “strictly necessary” statutory requirement as applicable to the facts in that judgment, CSIS cannot retain information that is not directly threat-related to the security of Canada unless such information can be related to a warranted target. The Court concluded that CSIS was acting unlawfully when retaining non-threat-related information under the “strictly necessary” qualifier past the warranted time limits.
The Government of Canada introduced the dataset regime through the National Security Act 2017 (NSA 2017) as a modification to the CSIS Act in July 2019. This regime authorizes CSIS to collect datasets that are likely to assist it in its duties and functions; that is, datasets that do not meet the “strictly necessary” otherwise required by s 12.
NSIRA’s review of the dataset regime is the first since the NSA 2017 came into force. This review examines and scrutinizes the governance and operationalization of the regime. In looking at the implementation of the regime, NSIRA also reviews the systems and processes in place for the ingestion, evaluation, query, and exploitation of datasets, a detailed description of which is provided in the Technical Annex A of this report.
Summary of the dataset regime in legislation
The CSIS Act’s (hereafter the Act) provisions governing the regime are found at sections 11.01 to 11.25, 21, 27 & 27.1 of the Act (henceforth referred to as the dataset regime). The Act defines a dataset as a “collection of information stored as an electronic record and characterized by a common subject matter.” The application clause at section 11.02 states that: “Sections 11.01 to 11.25 apply to every dataset that contains personal information, as defined in section 3 of the Privacy Act, that does not directly and immediately relate to activities that represent a threat to the security of Canada.”
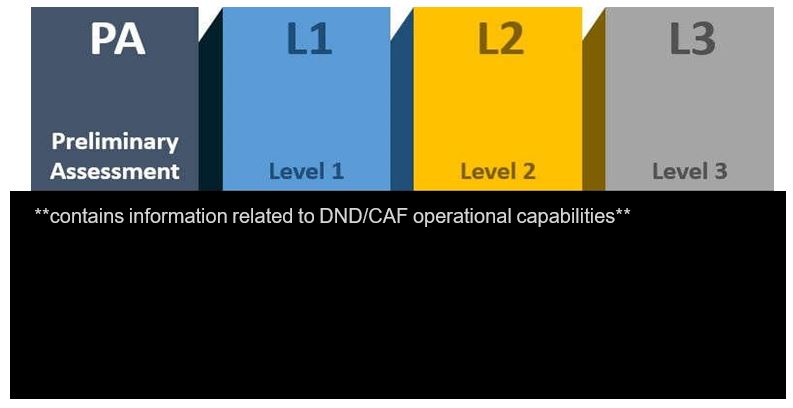
The level of authorizations and approvals for collection and retention of a dataset are proportionate with the level of privacy intrusion. For all categories of datasets, publicly available, Canadian, and foreign, CSIS may: “collect the dataset if it is satisfied that the dataset is relevant to the performance of its duties and functions under sections 12 to 16.” An additional, higher threshold exists for the retention of foreign and Canadian datasets where CSIS must establish that the collected dataset is “likely to assist” in the performance of its duties or functions.
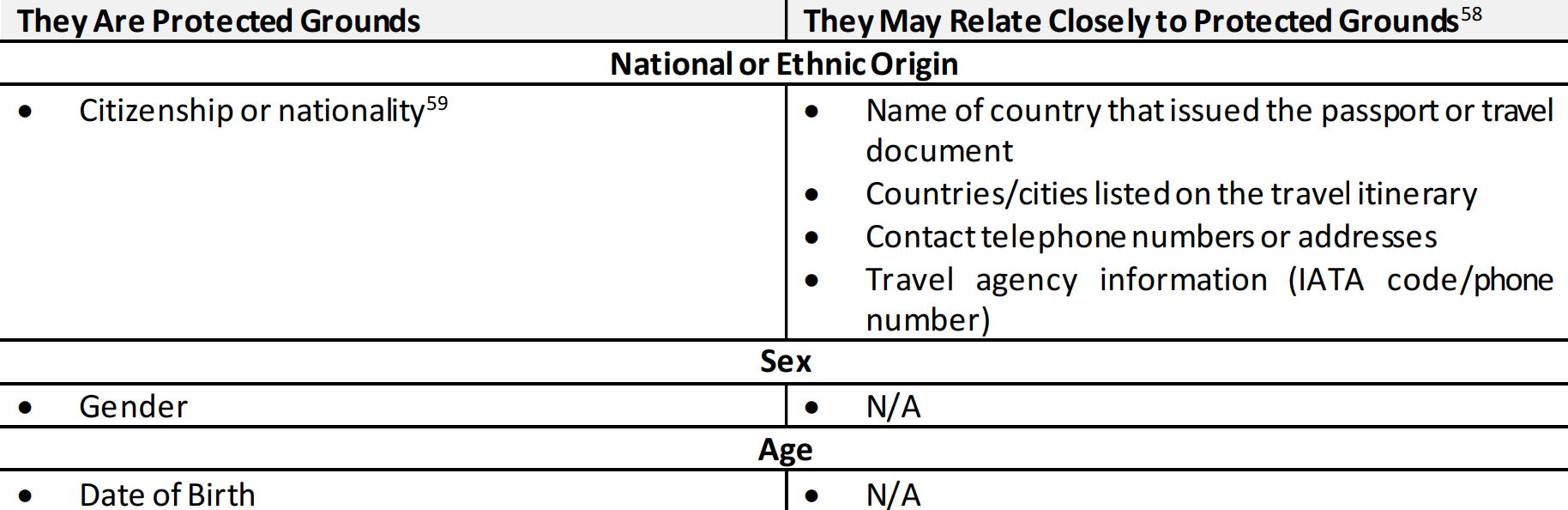
The legal framework for the publicly available datasets (PADs), the foreign dataset and Canadian datasets is summarized in the table below:
| Publicly Available | Foreign | Canadian | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | A dataset that was publicly available at the time of collection. | A dataset that predominately relates to individuals who are not Canadians and who are outside Canada or corporations that were not incorporated or continued under the law of Canada who are outside Canada. | A dataset that predominately relates to individuals within Canada or Canadians. |
| Collection | Threshold: Relevant to the performance of duties and functions under s. 12 to s.16 | ||
| Must belong to an approved class authorized by the Minister and approved by the Intelligence Commissioner (IC) | |||
| Evaluation | Within 90 days of the day on which it was collected (no query or exploitation): Designated employee shall delete any personal information that is not relevant to CSIS’s performance of its duties and functions. Designated employee may delete extraneous/erroneous/poor quality information; conduct translation and/or decryption, apply privacy protection techniques; any activity to organize the dataset. | ||
| Designated employee shall delete any information where there is reasonable expectation of privacy that relates to physical or mental health. | |||
| Designated employee to remove any information that relates to a Canadian or person in Canada. | Designated employee to delete any information that is subject to solicitor client privilege. | ||
| Retention | May retain for purposes of s. 12 to s.16. | Threshold: Must be likely to assist in the performance of duties and functions. | |
| Minister or Ministers designate authorize, followed by approval by the IC. | Minister approval followed by application for judicial authorization. | ||
| Retention period | No limitations (internal retention policy) | Maximum 5 years (can reapply) | Maximum 2 years (can reapply) |
| Query/Exploit | May query, exploit, and retain results for s. 12 to 16. | Designated employee may query or exploit (and retain results) to extent that is strictly necessary for s. 12, 12.1, and as required under s. 16. | |
| May query and exploit (and retain results) for s. 15. | |||
| Record Keeping | Record: – rationale for collection; – details of every exploitation; and – details of statutory authority under which query/exploit information is retained. Conduct random and periodic verification | ||
| Must: – Store and manage separately from other information; and – Limit access to designated employees and ensure that information is communicated only for performing duties under the act. | |||
| Exigent Circumstances | Director may authorize (subject to IC approval) the query of a dataset that has not been authorized if there are exigent circumstances that require the query to preserve life of safety of an individual or to acquire intelligence of significant importance to national security the value of which would be diminished or lost if CSIS were too comply with the authorization process. | ||
| Reporting | Report to NSIRA: – Any verification done as required by record keeping provisions. – Removal of information from a foreign dataset that concerns Canadians or persons in Canada. – Copy of the Director’s authorization for exigent circumstances query, the results of the query, and the actions taken after obtaining the results of the query. *NSIRA may report to the Director if it is of the view that query/exploitation of the dataset did not comply with the law. Director to send report along with any additional information to the Federal Court. Federal Court may issue a direction or order or take any other measure considered appropriate | ||
Governance
CSIS’s interpretation and application of the dataset regime
Finding 1: NSIRA finds that CSIS’s current application of the dataset regime is inconsistent with the statutory framework.
Finding 2: NSIRA finds that CSIS’s current approach to dataset information collection under section 12 risks the creation of a parallel collection mechanism, one that weakens section 12’s statutory thresholds and at the same time lacks the external oversight regime intended to protect personal information under the dataset regime.
The dataset regime sought to create a method of allowing the collection and retention of certain information that would not be possible pursuant to section 12 of the CSIS Act. CSIS was actively involved in advocating for this detailed regime and noted during the senate hearings that it (sections 11.01-11.24) was “quite a complex piece of legislation” which required that they work closely with the Department of Justice (hereafter Justice) to examine the “various processes that [they] could employ to make sure” that it was a very “charter compliant regime.” Having been so involved with the drafting of the regime, CSIS was thus well positioned to develop policies and procedures governing the collection, evaluation, query, exploitation and verification of datasets. At issue for CSIS was whether the dataset regime limits collection authorities of datasets under CSIS’s information collection mandates in section 12 (security intelligence), section 15 (security screening investigations), or section 16 (foreign intelligence). CSIS initially adopted the position that, in cases where the dataset was not directly and immediately related to threat activities, it had to be ingested under the section 11.01 regime (hereafter, CSIS’s initial position). This position did not affect the ability to collect information that directly and immediately related to threat activities under section 12.
[**redacted**] CSIS shifted its position to consider the dataset regime as, in effect, subordinate to the collection authorities in sections 12, 15, or 16 of the CSIS Act. In practice, CSIS relies on the dataset regime if and when it has determined that the information falls outside these collection authorities (hereafter, CSIS’s current position). This position reflects an evolution in understanding about the dataset regime’s scope.
CSIS’s application of the dataset regime as reflected in their policies, presentations, and NSA 2017 training materials more closely conformed to their initial position. However, by April 2022, CSIS adopted its current position on the application of the dataset regime, concluding also that the Court supported this interpretation. CSIS now regards the dataset regime as allowing the collection and use (searches) of datasets pursuant to section 12, followed by their retention pursuant to the dataset regime. CSIS has continued to evolve its current position to allow for broader collection and retention under section 12.
Notably, section 12 includes conditions on collection (and retention) that are more demanding than the equivalent thresholds for collection and retention under the dataset regime. Under section 12, an investigation depends on a reasonable grounds to suspect a threat to the security of Canada, and information collection and retention only to the extent “strictly necessary.” The dataset regime, for its part, permits collection where CSIS is “satisfied that the dataset is relevant to the performance of its duties and functions” under sections 12 to 16. Retention of foreign and Canadian datasets is permitted on the threshold of “likely to assist” the enumerated CSIS mandates. Section 12 and the dataset regime also differ in terms of control regimes. CSIS retains under section 12 without any external oversight. Retention under the dataset regime of Canadian datasets requires the Court’s authorization, retention of foreign datasets requires the IC’s approval.
The dataset regime was created for the purpose of broadening carefully-regulated dataset collection and retention in circumstances where the section 12 “strictly necessary” threshold could not be met. NSIRA noted, however, that in the period since the evolution of CSIS’s current position, discussed above, CSIS’s operationalization of the dataset regime and their understanding of the application of the regime seems to have significantly broadened the scope of information captured under its section 12 authorities. This evolution is discussed in the case study at the end of this report.
The [**redacted**] formerly the Data Management and Exploitation or DMEX) is a branch whose primary function is the governance of the dataset regime. By June 2023, CSIS informed NSIRA that [**redacted**] would now move to fully prioritize s. 12 collection over dataset regime collection. CSIS stated that absent a less prescriptive legislative framework for dataset collection, CSIS would not be collecting datasets unless the intention was to exploit them. CSIS then presented NSIRA with a clear example of a foreign dataset within the meaning of the dataset regime and indicated that since there was a possibility that there may be hostile actors on the list, it could be collected pursuant either to section 11.05 of the dataset regime or collected pursuant to s. 12. It could also be searched under section 12, with any threat related search results retained under section 12 and the remainder of the list destroyed.
Two concerns stem from CSIS’s evolving approach to datasets illustrated by the case studies that follow. First, the ingestion of datasets under section 12 may now, in practice, reflect a broadened understanding of the section 12 “reasonable grounds to suspect” and “strictly necessary” thresholds. The standards now invoked to justify the collection and retention of some datasets putatively under section 12, are closer to the “satisfied” and “likely to assist” thresholds for the dataset regime. NSIRA acknowledges that some information meeting the definition of a dataset, i.e. the collection of information stored as an electronic record and characterized by a common subject matter, may fall within section 12 collection and use authorities, e.g. a list of Canadian Extremist Travelers. However, NSIRA’s concerns relate to when s. 12 authorities are interpreted to allow for the collection and use of personal information that is not directly and immediately related to activities that represent a threat to the security of Canada. This approach is inconsistent with the statutory framework and risks the creation of a parallel collection mechanism, one that weakens section 12’s statutory thresholds and at the same time lacks the external oversight regime intended to protect personal information under the dataset regime.
Second, a multi-stage vetting process necessarily follows from an interpretation of the CSIS Act in which the dataset regime applies only where datasets (meeting the section 11.02 definition) cannot be collected or retained under the section 12, 15, or 16 mandates. Not least, there will be a preliminary phase in which CSIS will need to decide which authority applies and whether (because no other collection or retention authority is available) the dataset must be processed under the dataset regime. Without careful guidance, there is a considerable risk of confusion as to what may be done with the dataset during this triage vetting, especially since that vetting process is not expressly anticipated by the Act. It is not clear that the Act accommodates a parallel and separate process in which a dataset is collected under section 12, searched for intelligence purposes, and only then transferred for retention under the dataset regime. This would seem to render the exigent search powers in s 11.22 redundant. While NSIRA was not able to fully confirm the sequence of events, the Canadian dataset judicial authorization case study discussed in the next section reflects the risk of confusion.
Canadian Dataset Judicial Authorization
Finding 3: NSIRA finds that CSIS failed to fully apprise the Court on their interpretation and application of the dataset regime. CSIS should have sought clarification from the Court as to its views on the precise conduct permissible prior to invocating the dataset regime.
Finding 4: NSIRA finds that when conducting queries in exigent circumstances, CSIS retained information that did not meet the section 12 strictly necessary threshold.
From [**redacted**], CSIS collected [**redacted**] individuals [**redacted**] contained personal information of [**redacted**]. The datasets were provided to CSIS from multiple government [**redacted**] departments [**redacted**]. These datasets were [**redacted**] received by the [**redacted**] Unit and therefore [**redacted**] deemed collected pursuant to s. 12. However, CSIS then sought to retain the pursuant to the dataset regime, requiring authorization by the Federal Court (FC). The result was the first judicial authorization decision under the dataset regime. There are two concerns about the management of this dataset.
Initial consideration of the dataset under section 12
In the lead-up to this authorization, there appears to have been considerable uncertainty as to how this dataset might be used. The evidence shows that [**redacted**] received the [**redacted**] through the Security of Canada Information Disclosure Act. [**redacted**] considers all information disclosed and collected by their branch as section 12 information. Upon receipt of the dataset, [**redacted**] was not aware of the discussions occurring within other branches regarding the possibility of applying to the Court for the retention of [**redacted**] through judicial authorization. [**redacted**] treated the information much like any other section 12 information and searched at least two of the names [**redacted**] within CSIS’s operational database, [**redacted**], one of which yielded results.
NSIRA was initially informed that these searches did not amount to queries because they were not searches within the [**redacted**], rather they were searches of names from the [**redacted**] against [**redacted**]. NSIRA was also informed that the searches were not queries because they were not for “the purposes of obtaining intelligence” as defined in the Act, since the results of the searches were not reported [**redacted**]. In [**redacted**] discussion with CSIS, NSIRA received conflicting information that demonstrated internal contradictions and confusion on these points.
In the cover letter to the affidavit for judicial authorization (JA) for a Canadian dataset filed with the Court, Counsel notes that “the Service’s initial collection and use of this information as described in the affidavit falls with the scope of the service’s [**redacted**]. In the affidavit, CSIS stated that “… [**redacted**] verified whether this collection of information was already within Service holdings and assessed the potential intelligence value for its investigations. No searches were conducted for intelligence purposes…” In a previous draft of the affidavit, the chief of DMEX had expressed their concern regarding this wording of the draft affidavit.
They noted that “We have already clearly stated that the datasets were initially collected [**redacted**] authorities. We can also say that checks were done under those authorities but immediately ordered stopped once s.11 was invoked (which happened quickly).” NSIRA could not determine if searches of names from the list against CSIS’s operational system were conducted with the objective of “verifying” whether the “collection of information was already with Service holdings.” In examining this issue, it became apparent that there were multiple opinions and conflicting narratives regarding what actions were taken upon receipt of the dataset and what CSIS perceives as permissible when dataset information is collected through s. 12.
The Federal Court found in its authorization decision that it was reasonable to collect the dataset pursuant to s. 12, in the circumstances of this matter. The Court notes that “the decision was taken to invoke the dataset regime and to request approval to query the information under the exigent circumstances provision in s. 11.22 of the Act.” It is unclear if the Court knew the full record of uncertainty about what could be done with the dataset in the interim between collection under section 12 and the commencement of the dataset regime retention process. CSIS should have fully apprised the Court of this uncertainty (including the conflicting narratives regarding how the data was and may be used) and sought clarification from the Court as to its views on the precise conduct permissible prior to the invocation of the dataset regime.
This is especially the case since, both in the decision and during the hearings for the JA, the Court expressed its concern that the classes authorized by the Minister and approved by the IC were too broad. The Court added that “just about anything under the sun could be captured by one of those classes.” Yet, CSIS assured the Court more than once that information collected was pursuant to s. 11.05 and was protected by the safeguards of the regime, that the information had high access control and could not be queried or exploited. Accordingly, the Court was informed that while the classes are broad, the regime provides the necessary safeguards to protect the privacy of Canadians. This response deemphasized the degree to which information from the dataset might be used during the triage period. Again, this discussion presented CSIS with the opportunity to judicially test its application of the interpretation of the dataset regime before the Court. CSIS could have informed the Court that these safeguards may not necessarily be in place where information is collected pursuant to section 12 prior to a pivot to the dataset regime as the retention authority. It appears that CSIS chose to carry this legal uncertainty at the risk of receiving a constraining interpretation of the regime by the Court.
Querying and retention under exigent circumstances
Notably, once CSIS initiated the dataset regime process, the dataset for which the JA was sought was the subject of an authorization and approval pursuant to s. 11.22 exigent circumstances. CSIS sought and received authorization from the Director and approval from the IC to query the datasets. As per the requirements of section 11.13(2) of the Act, CSIS included in its application for JA the contents of the exigent circumstances authorization, the results of the authorized query, and any actions taken after obtaining these results. This information was also provided to NSIRA as required by s. 11.25(c) of the Act.
CSIS queried the names [**redacted**] CSIS retained [**redacted**] partial matches and reported them in their section 12 operational system. In examining the queries conducted, NSIRA found that the initial searches were extremely broad with many name [**redacted**] searched using extensive use of [**redacted**], and a very large margin for date of birth [**redacted**].
These broad queries resulted in numerous “hits” against the list. For example, [**redacted**] were all considered by the CSIS analyst as appropriate search results against [**redacted**]. These names were then searched in [**redacted**]. Information from an exigent query may be retained if “carried out under section 12”, imposing that section’s “strictly necessary” threshold. Despite there being no results for any of full [**redacted**] names in [**redacted**], CSIS determined that the absence of the names in its operational system meant that the names could not be eliminated as “a possible candidate for identification” and that “ultimately, those possible matches that cannot be excluded will be reported to the desk and retained under s. 12 for further investigation.”28 Similarly, should the name of [**redacted**] be too common to rule out, CSIS retained that name as strictly necessary.
The results of these unnecessarily broad queries did not meet the strictly necessary threshold for retention. [**redacted**] In March 2022, CSIS reported that [**redacted**] has determined it would not pursue investigative steps regarding the results (reported in [**redacted**]) absent additional information” and that the [**redacted**] results retained were “captured in their entirety for retention in the event that the dataset is destroyed.” The exigent circumstances queries cannot be used to circumvent the retention obligations that would apply under s.12 or as means to retain information pending the outcome of the judicial authorization.
Recommendation 1: NSIRA recommends that in the next judicial authorization application for a Canadian dataset CSIS put its current position on the application of the dataset regime before the Court, including any use of the information prior to the decision to retain under the dataset regime.
Recommendation 2: NSIRA recommends that CSIS immediately destroy any record containing names retained pursuant to the exigent circumstances queries as they do not meet the strictly necessary threshold.
Gap in the legislation
Finding 5: NSIRA finds that the lack of explicit time limits in section 11.17 of the dataset provisions governing foreign datasets has resulted in datasets being retained for multiple years pending a decision by the Minister or the Minister’s designate (the CSIS Director).
The dataset regime added many detailed provisions to the CSIS Act. Despite the complexity of the regime, NSIRA noted gaps in the legislation. The provisions of the Act governing the authorization of the retention of foreign datasets do not provide a time limitation for the Minister or the Minister’s designate to authorize the retention of a foreign dataset. Prior to the coming into force of the dataset regime, CSIS had accumulated bulk data that would no longer be compliant pursuant to the new regime. Accordingly, the transitional provisions of Bill C-59 recognized the presence of this information and deemed it collected on July 13, 2019 as per the Order in Council. CSIS then had 90 days to evaluate the foreign datasets it wished to retain, and determine if it wished to evaluate and seek judicial authorization for any bulk Canadian information.
On October 11, 2019, CSIS submitted ten applications for authorization to retain foreign datasets to the Director. The first dataset authorization was approved by the IC on December 16, 2020. In their December 16, 2020, decision, the IC made recommendations regarding the contents of the authorization. One of these recommendations concerned how these datasets collected in [**redacted**] remain likely to assist CSIS in the performance of its duties and functions. The [**redacted**] remaining datasets that had been submitted to the Director for authorization were then edited to include the information requested by the IC. These edits were included as an appendix to the applications. Despite the fact that the edits included material information regarding how the datasets remain likely to assist CSIS in its duties and functions, they were not considered resubmissions to the Director. As of December 2022, CSIS had only submitted two more requests for approval to the IC, totalling three approvals in three years.
CSIS asserted that there were no statutory deadlines that would limit the Director from having these applications for years and that resourcing constraints meant that the requisite edits would take time to complete. This legislative gap has allowed for a parallel mechanism of retention of data that is otherwise strictly governed. While CSIS cannot ingest, query, or exploit the data until the IC approves it, the gap in legislation allows them to query the data in exigent circumstances as per section 11.22 of the CSIS Act.
Furthermore, the legislative gap allowing the authorization request to remain before the Director, un-actioned for years, puts into question how CSIS will meet the “likely to assist” threshold tied to the utility of these datasets. It should be noted that as of April 2023, the dataset approved in 2020 had not been queried, while the one approved in 2021 has been queried only [**redacted**]. This gap in legislation was also noted by the IC, stating: “I am unconvinced that Parliament’s intent was for there to be such a long delay between a request from CSIS for authorization to retain a foreign dataset and the Director’s authorization.”
Recommendation 3: NSIRA recommends that Parliament legislates a time limitation for the authorization of a foreign dataset by the Minister or Minister’s designate.
CSIS dataset Policies
Finding 6: NSIRA finds that CSIS runs the risk of collecting information that is publicly available but for which there may be a reasonable expectation of privacy.
Finding 7: NSIRA finds that CSIS’s policies governing the collection and retention of Canadian and foreign datasets do not align with its current interpretation of the dataset regime.
Finding 8: NSIRA finds that CSIS does not have a policy governing the handling of transitory information. In addition, the existing Interim Direction [**redacted**] does not provide employees with sufficient instruction, which may result in CSIS retaining information that would otherwise be subject to the dataset regime.
CSIS codified in policy its commitment during the enactment of Bill C-59 to not collect hacked or stolen datasets. It acknowledged that there would be a “much higher expectation of privacy associated with those datasets,” and noted that even if adversaries had access to this information CSIS would hold itself to “a higher standard.” However, overall CSIS found itself struggling to implement the provisions of the Act and align its policies and procedures with it.
NSIRA flags four specific concerns. First, the policy center for datasets is the Data Management and Exploitation Branch (DMEX), recently restructured and renamed as [**redacted**]. The dataset policy suite [**redacted**] includes a number of policies pertaining to the identification, collection and retention of section 11.01 datasets. Although the commitment to not collect stolen, hacked or leaked datasets is codified in [**redacted**], there is no corresponding requirement to ensure that information contained in publicly-available datasets (PADs) does not contain information for which there is a reasonable expectation of privacy. Yet, this requirement is especially pertinent when considering the strong emerging market for data purchased through data brokers and the risks associated with purchasing commercially available information that may have been unlawfully collected by said brokers.
Second, as discussed earlier, the shift in CSIS’s position on the relationship between datasets and its regular collection powers has resulted in discrepancies between what information amounts to s.11.01 datasets and what information may be collected pursuant to s. 12. CSIS’s interpretation of the applicability of the dataset regime was reconsidered in 2021, two years after the dataset governing policies were developed. The existing policy suite aligns more with CSIS’s initial position. This has resulted in a policy suite that no longer aligns with CSIS’s current position on the implementation of the dataset regime (discussed above) or with the current structure of the [**redacted**] branch.
Third, the [**redacted**] policy sought to guide and educate employees on the dataset regime. It also placed the onus on “employees who collect the dataset” to determine the appropriate collection authority. This further emphasizes the importance of training received by employees, discussed further below.
Fourth, in 2021, CSIS developed an Interim Direction to support its section 12 collection of datasets. The introduction of this Direction corresponded with the pivot in the interpretation and operationalization of the dataset regime, discussed in section 4 above. The Direction allows for collection of electronic information that has been assessed to be threat-related where threat and non threat information are inextricably co-mingled. It allows for the temporary retention of this information in these circumstances. The direction does not provide any information as to what amounts to inextricably co-mingled information but allows for its sequestered retention for up to [**redacted**] with extension. This non-threat related information would have been subject to the dataset regime, yet the Direction is silent on the requirements of the dataset regime including the connection and relationship to that regime’s 90 day evaluation period. In practice, CSIS does not have a central repository for temporary information, which results in this information being held on unit shared drives absent centralized monitoring, access controls, and auditing. This, along with the constant rotation of employees, lack of training on the Direction, the absence of clear points of accountability and responsibility in the policy, and the [**redacted**] time limitation which greatly exceeds the 90 days limitation in the dataset regime, creates a situation where CSIS risks retaining depositories of information that would otherwise be subject to the dataset regime.
Recommendation 4: NSIRA recommends that CSIS meaningfully analyze and document any possible reasonable expectation of privacy when evaluating publicly available datasets.
Recommendation 5: NSIRA recommends that CSIS develop:
- Guidelines regarding the implementation of section 6 of the Interim Direction [**redacted**] that also include consideration of how the Direction’s retention rule is to be reconciled with the 90 day evaluation period in the dataset regime; and
- A policy governing the handling of transitory information.
Information Management and Retention
Finding 9: NSIRA finds that CSIS information management practices are responsible for multiple compliance incidents and currently create duplicates of datasets within CSIS’s systems.
Finding 10: NSIRA finds that, as of August 2023, CSIS did not comply with the dataset provisions in the CSIS Act because it retained Canadian information extracted from foreign datasets, and foreign information amounting to a dataset.
Finding 11: NSIRA finds that CSIS did not comply with the dataset provisions in the CSIS Act because it retained Canadian information and referenced it as recently as 2022. This information should have been destroyed upon coming into force of the NSA 2017, in July, 2019.
Finding 12: NSIRA finds that CSIS has not exhaustively scanned all of its systems to identify information that is subject to the dataset regime so that it may be processed in a compliant manner.
From 2018-2019, CSIS conducted an inventory of its holdings to identify information that would be subject to the dataset regime—and therefore need to be deleted— once the regime came into force. CSIS identified several categories of operational reports containing collected Canadian or Foreign information, and developed caveats to insert into the reports indicating that information had been removed.
For foreign datasets, CSIS senior management identified which foreign datasets would be submitted for authorization. Technical analysts conducted a number of exercises on the foreign datasets to test their ability to identify and extract Canadian information as would be required under the dataset regime. These exercises led to the creation of multiple [**redacted**] containing the extracted Canadian data, which was then uploaded [**redacted**] for storage in CSIS’s corporate repository. In doing so, CSIS retained copies of data that should have been deleted.
According to CSIS, duplication is a requirement of CSIS’s information management policy (see Annex A). For example, when a query of a dataset is conducted, CSIS’s information management policy requires analysts to attach the results of the query to the report that gets saved in the operational system. Analysts are also required to save a copy of that report and its attachments to [**redacted**], CSIS’s corporate repository. This has contributed to compliance issues. It also increases the difficulty of deleting information when compliance incidents arise or if CSIS has retained information that is not strictly necessary. Additional examples of where data duplication occurs are described in Annex A.
On September 5, 2019, CSIS assured the Minister that it “undertook significant efforts to ensure compliance with the coming-into force of the dataset framework created by Bill C-59” and that “as a direct result of this exercise, a number of Canadian and foreign datasets were assessed as not meeting the criteria for retention under section 12 or the `likely to assist’ retention threshold under the new dataset framework. These datasets were therefore destroyed prior to coming-into force.” In September 2021, CSIS asserted to NSIRA that all the foreign datasets that were not before the Director for authorization were destroyed.
In [**redacted**] a former DMEX employee discovered [**redacted**] containing a foreign dataset, which had been collected prior to the coming into force of the dataset regime and subsequently submitted for Ministerial authorization. [**redacted**] contained the entire pre-evaluation dataset, including Canadian information. In [**redacted**] another DMEX employee discovered Canadian information extracted from foreign datasets [**redacted**] accessible only by designated employees. These latter records included Canadian information and foreign samples extracted from [**redacted**] foreign datasets, [**redacted**] of which were pending Ministerial authorization, [**redacted**] of which was already approved by the IC, and of [**redacted**] which were destroyed in their entirety prior to the coming into force of the regime. CSIS destroyed this information because it was unlawfully retained.
These incidents prompted DMEX to conduct a file review “to determine what steps has been taken prior to coming into force of NSA 2017 and what remediation efforts might be necessary. Although employees had been directed to delete potential dataset candidates for which it would not seek authorization to retain with the coming into force of NSA 2017 in July 2019, similar steps had not been taken to direct employees to identify and destroy other copies of datasets and any Canadian or other records removed from these datasets prior to coming into force of NSA 2017 or in the 90 day evaluation period that followed.” DMEX then instructed employees to “conduct a thorough search [**redacted**].” The outcome of these searches was that significant additional Canadian and foreign information was found. This included information pertaining to the [**redacted**] Dataset discussed below. DMEX reported these multiple compliance incidents to CSIS’s review and compliance branch by submitting a fact finding report with supporting material The concluding comments of the report state that a “fulsome” effort was made to identify residual data however [**redacted**] ”.
In October 2022, NSIRA conducted searches of CSIS’s corporate repository and found [**redacted**] files containing tens of thousands of entries of Canadian personal information extracted from [**redacted**] foreign datasets, including information extracted from datasets that have been destroyed, approved by the IC, and pending authorization. The files also contained foreign information. The Canadian information was extracted as part of the exercise to prepare for the coming into force of the Act and should have been destroyed.
NSIRA enquired as to why these files containing Canadian information extracted mostly from destroyed foreign datasets remained in CSIS’s corporate repository and the legal authority under which they are retained. CSIS failed to provide an adequate explanation as to this legal non-compliance, they stated that the information was part of a project in preparation for the coming into force of the dataset regime, and that:
“those Canadian records continue to exist in the PA’d file even though the original datasets were either all destroyed or sequestered pending Ministerial Authorisation. While certainly contrary to current (since June 2019) s.11 obligations, at that time, this work and retention would have been done under (implicit) s.12 authorities. As this predates the dataset framework, we are unclear if this presents a legal or compliance risk. [**redacted**]
CSIS stated that the records were retained “appropriately at the time, pre C-59, under s.12 implicit authorities”. It is unclear how CSIS distinguishes between the information found by NSIRA and that found by DMEX in [**redacted**] mentioned at paragraph 55 above. As of August 2023, information that NSIRA found in October 2022, containing Canadian and foreign data was being retained by CSIS, in contravention of its legal obligations pursuant to the dataset provisions in the CSIS Act.
NSIRA also searched for operational reports that had been identified prior to the coming into force of the dataset regime as containing information that would amount to Canadian datasets. NSIRA found a number of reports where the information had indeed been deleted and a caveat added. However, NSIRA found [**redacted**] report related to [**redacted**] dataset containing the [**redacted**]. It should be noted that the operational report in question was not sequestered, rather was accessible to all those using the system and was referenced in a report as recently as August, 2022. This would have amounted to a query of what should have otherwise been a Canadian dataset.
NSIRA requested that CSIS provide the authorities under which it is retaining this information. CSIS initially responded that they could not find the report as it had been previously destroyed. Shortly thereafter, CSIS stated that they have found the report and were treating it as a compliance incident. Upon searching the operational system once more, NSIRA found another report containing the [**redacted**] Both reports found by NSIRA contained information that would otherwise amount to a Canadian dataset, [**redacted**]. By retaining this Canadian information, CSIS did not comply with legal obligations pursuant to its dataset regime provisions in the CSIS Act.
The non-compliant information found by NSIRA (Canadian and foreign information from foreign datasets and Canadian information in operational reports) was discovered following CSIS’s initial pre C-59 scan of holdings reported to the Minister and following CSIS’s “thorough search of personal and shared holdings” due to the compliance incident in 2022. CSIS has not exhaustively scanned all of its systems to identify information that is subject to the dataset regime so that it may be processed in a compliant manner.
Recommendation 6: NSIRA recommends that CSIS cease to create duplicates of the information reported in the operational system.
Recommendation 7: NSIRA recommends that CSIS immediately destroy Canadian and foreign dataset information that is not strictly necessary to retain. This information no longer falls within the legal 90 day evaluation period and retaining it pursuant to the dataset regime is no longer a possibility.
Recommendation 8: NSIRA recommends that CSIS conduct an exhaustive scan of its operational and corporate repositories to identify and destroy any non-compliant information.
Training and Resourcing
Training
Finding 13: NSIRA finds that the training required to become a designated employee to evaluate, query, and exploit s. 11.01 datasets offers clear information on collection and retention requirements.
Finding 14: NSIRA finds that CSIS operational personnel, including those predominantly dealing with bulk information collection, have not received adequate training allowing them to identify when collected information may fall within the dataset regime.
Prior to the coming into force of the NSA 2017, including the dataset regime, CSIS developed and implemented specialized training for employees to be designated pursuant to s. 11.06(1) of the CSIS Act, and mandatory Bill C-59 training for all operational employees. CSIS also developed and delivered a number of presentations to assistant directors, management, relevant branches, other government departments, and the Federal Court. This suite of training and presentations align with CSIS’s initial position, discussed above, on the applicability of the dataset regime.
CSIS currently offers two mandatory training courses for the designation of employees. These courses emphasize the distinction between s. 12 “strictly necessary” information and what may be collected pursuant to the dataset regime “likely to assist threshold.” The courses require that an employee familiarizes themselves with the standard operating procedures and requirements of the regime. While online training may not be the ideal training method, the training content along with the mix of standard and scenario based questions offered employees clear instruction on the regime and its requirements.
As noted above, CSIS also implemented mandatory training for all operational personnel. CSIS developed most of the dataset regime training prior to and immediately following the coming into force of the NSA 2017. As discussed at Section 4 of this report, CSIS’s understanding of its statutory obligations pursuant to the regime and how these obligations are perceived and implemented, has changed. The result is that the mandatory training received on a once-and-done basis by operational personnel in 2019 does not align with and may in fact contradict CSIS’s current operationalization and implementation of the regime.
Additionally, the very little training that is received by operational personnel does not allow collectors to determine what information is a dataset despite the onus placed on them to do so. This has resulted in individuals who deal with bulk information collection not being sufficiently aware or trained on the dataset regime.
For intelligence officers, CSIS developed a presentation on the dataset regime as part of the [**redacted**], the mandatory course offered to intelligence officers within a few years of their career [**redacted**]. Initially, when CSIS implemented the training program, employees had to work in groups in a series of workshops to identify the properties of s. 11.01 datasets, including distinguishing them from s. 12 datasets and relating Canadian datasets to approved sets of classes. This training was offered as an instructor-led course until March 2020, after which CSIS removed the workshop component from the updated training program, effectively eliminating any scenario-based questions and exercises. While CSIS has told NSIRA that it is currently working on updating the program, the current training offers little opportunity for collectors to distinguish s.11.01 datasets from s. 12 information.
NSIRA finds that CSIS’s once-and-done approach to training on datasets has resulted in a lack of understanding and sensitization of employees to the dataset regime. CSIS should increase its efforts to sensitize its collectors to the dataset regime requirements and particularities while encouraging them to contact the data exploitation branch when in doubt.
Recommendation 9: NSIRA recommends that CSIS develop and deliver scenario-based workshops to train operational personnel on CSIS’s current application of the dataset regime so that they can engage subject matter experts as necessary.
Resourcing
Finding 15: NSIRA finds that CSIS has not prioritized resourcing the technical unit responsible for the evaluation, query and exploitation of Canadian and foreign datasets.
Finding 16: NSIRA finds that CSIS has not devoted sufficient resources to improving the current technical systems or developing new ones that are equipped to support bulk data use.
In NSIRA’s past review work, issues of training and resourcing often arise together and correlate to an organization’s commitment to a particular program or branch. In April and in November 2022, CSIS informed NSIRA that the Operational Data Analysis Center (ODAC), housed within DMEX and responsible for the technical implementation of the dataset regime including the ingestion, query, and exploitation of datasets was [**redacted**] percent vacancy respectively.
In 2020, no employees were designated for the query or exploitation of datasets despite the authorization and approval of the first foreign dataset. CSIS’s approach to ensuring that they have individuals who are designated and therefore lawfully able to query and exploit information was reactive. In a 2020 verification report provided to NSIRA, CSIS stated that first foreign dataset was authorized by the Director and approved by the IC, yet “there were no employees designated for queries of exploitation of s. 11 Canadian or foreign datasets.
Consequently, no queries or exploitations” of the dataset were conducted. The fact that CSIS had sent its first dataset approval to the IC without having resourced its specialized unit and enabled them to conduct the potential requisite queries and exploitation of the dataset is indicative of [**redacted**]. It took CSIS almost [**redacted**] years to designate an employee for query and exploitation of foreign and Canadian datasets. With the exception of the queries conducted pursuant to the exigent circumstances, no other queries were conducted in 2021.
In November 2022, CSIS expressed concerns that the 90 days provided for evaluation in the Act is too inhibiting and has often resulted in missed collection opportunities. [**redacted**]. Upon further discussion NSIRA was informed that [**redacted**]. Similarly, in 2023 NSIRA was again informed of CSIS’s inability to work within the parameters of the current legislation; in this instance, CSIS had greater resources but had chosen to allocate them to [**redacted**] collection rather than the dataset regime.
The resourcing issues are further compounded by CSIS’s current technical ecosystem. The lifecycle of a dataset involves many different digital tools and systems, [**redacted**] Moreover, these tools and systems can only be customized and maintained by people with niche technical expertise. These compounding factors have created a situation where DMEX employees have limited options for conducting data exploitation, and this has affected the utility of all three categories of datasets. Based on briefings with technical experts and technical demonstrations, it is evident that the current systems are not designed to support bulk data use in a compliant manner.
Recommendation 10: NSIRA recommends that CSIS prioritize resourcing the technical unit responsible for the evaluation, query and exploitation of Canadian and foreign datasets.
Recommendation 11: NSIRA recommends that CSIS prioritize the improvement of current technical systems or development of new systems, equipped to support compliant bulk data use.
Case Study: [**redacted**]
Finding 17: NSIRA finds that CSIS collected information in relation to activities that could not on reasonable grounds be suspected to have constituted a threat to the security of Canada and the collection, analysis and retention of which was not strictly necessary.
Background
[**redacted**]
[**redacted**]
On [**redacted**], CSIS sent a brief to the Privy Council Office and Public Safety outlining the information in [**redacted**] noting that prior [**redacted**].
CSIS [**redacted**]. The brief discusses the possibility of collecting the dataset under section 11, utilizing the 90-day evaluation period to assess whether it is a publicly available or Canadian dataset, and “if retaining and using the dataset for analysis will help ensure the security of Canada.”
The following day, [**redacted**].
[**redacted**], the Director General of the Data Management and Exploitation branch and of [**redacted**] submitted a co-drafted Memo to the Deputy Director of Operations (DDO) seeking the authorization to collect [**redacted**] pursuant to section 12 of the CSIS Act. The memo provides a summary of [**redacted**]. The memo notes [**redacted**] concerns regarding [**redacted**]. While the memo outlines the contents of the dataset as described [**redacted**], it fails to mention [**redacted**] within the database [**redacted**] likely stolen.
The memo quotes [**redacted**]. This statement again contradicts [**redacted**] assessment that information was likely collected for [**redacted**]. Based on that statement, the memo argues: [**redacted**].
Upon receipt of the memo, the DDO requests [**redacted**] ” In response, the DDO notes her concerns that [**redacted**] found no evidence suggesting that the [**redacted**]. The DDO further states that she will accept that the information “may indeed assist” CSIS’s investigation and that while no evidence of [**redacted**], “it is more likely than not” that this is the type of information [**redacted**] “would be interested in.” The DDO approved the collection pursuant to section 12 [**redacted**], CSIS received and ingested the Canadian [**redacted**].
[**redacted**]” It is unclear how this assessment was made, as it does not align with CSIS’s analysis of the [**redacted**], which was used to develop a CSIS Case Report, circulated to partners in government. The report states: “the portion of the dataset referencing Canadians appears [**redacted**]. The brief further notes that [**redacted**]. It should be noted that following the distribution of the Case Analysis Brief, CSIS has not conducted any further intelligence analysis or reporting on the dataset.
Analysis
When CSIS became aware of [**redacted**], the initial discussions focused on the potential collection of the information pursuant to the dataset regime provisions and utilizing the 90 day evaluation period to determine the scope of the dataset, whether it would be a Canadian, foreign, or publicly available dataset. It remains unclear to NSIRA why or what led the discussion to focus instead on a section 12 collection.
At the point of collection, CSIS had limited information regarding the dataset. Much of this information was also conflicting. [**redacted**]. Unfortunately, the full scope of this information was not presented to the DDO when seeking approval for collection pursuant to s.12.
Section 12 of the CSIS Act requires that “The Service shall collect by investigation or otherwise, to the extent that is strictly necessary, and analyse and retain information and intelligence respecting activities that may on reasonable grounds be suspected of constituting threats to the security of Canada.” The threshold to be met is reasonable grounds to suspect. The Supreme Court of Canada has defined a reasonable suspicion as “something more than mere suspicion and something less than a belief based upon reasonable and probable grounds.” It is a “robust standard,” which is “determined by the totality of the circumstances based on the objectively discernable facts.”
Applying the Supreme Court of Canada’s jurisprudence regarding the reasonable suspicion standard to the case at hand, CSIS did not provide any evidence or intelligence to support that the information [**redacted**]. In its analytical tools [**redacted**]. NSIRA found no evidence to support this statement at the point of collection, nor could CSIS explain how they reached said conclusion. That is to say, there were no objectively discernable facts to support that the dataset was indeed connected to a threat to the security of Canada. Rather, CSIS’s explanations to NSIRA, as well as the written records, focus on the potential utility of the information [**redacted**]. CSIS could not provide sufficient evidence to demonstrate how the collection of the information would be strictly necessary pursuant to s. 12. This is best articulated by the DDO’s comments stating that she is “not sold on the rationale” presented to her in the briefing note, but that she was convinced that given the importance of such information to [**redacted**] “it may indeed assist our [**redacted**] investigation of the threat represented [**redacted**]” NSIRA does contend that the information may be of use to [**redacted**] and the analysis of the dataset may be of use to CSIS. However, this dataset does not meet the strictly necessary threshold. Rather, it may meet the s. 11.05 threshold of “relevant to the performance of its duties and functions.”
Furthermore, the CSIS memo to the DDO did not disclose [**redacted**] belief that some of the information was not publicly available and that [**redacted**] may have been “stolen” [**redacted**]. Instead, it focused on [**redacted**]. The memo drafters used [**redacted**] statements to support their belief that there were ties to threat actors [**redacted**]. [**redacted**]. There was no preliminary assessment conducted by CSIS of the dataset as they did not have access to it. [**redacted**] stated [**redacted**] likely “stolen.”. Yet, there was no analysis of the privacy implications of the collection, nor an analysis on whether the collection of this dataset pursuant to section 12 may require a warrant.
Upon collection of the information CSIS analysed the dataset. It should be emphasized that this would have amounted to an exploitation of what should have otherwise been a Canadian dataset.
[**redacted**] the Data Management and Exploitation branch engaged [**redacted**] on the issue of retention of the dataset in light of the requirements in the policy.
[**redacted**]. This statement directly contradicts CSIS’ own assessment of the dataset, which states that [**redacted**]. It proceeds to justify retention by noting that [**redacted**].
A plain dictionary reading of the words “strictly necessary” in s. 12 of the CSIS Act would render a requirement that the information be “rigidly” “indispensable.” However, CSIS did not demonstrate in its justification how the information in the dataset is indispensable to its investigation. Rather, there is a “just in case” type argument put forward that states that it is important to retain the information as it could help a future targeting trend analysis. This justification may meet a likely to assist threshold but does not meet a strictly necessary threshold.
CSIS informed NSIRA that there has been no decision regarding the retention of the dataset, [**redacted**]. NSIRA also learned that should another relevant dataset or associated information arise in the future, at that point [**redacted**]. The dataset is currently in a controlled access shared drive, however no measures are in place to prevent its duplication or movement to other locations.
Recommendation 12: NSIRA recommends that CSIS immediately destroy the case study dataset it collected pursuant to section 12 as it does not meet the statutory thresholds. This information no longer falls within the legal 90 day evaluation period and retaining it pursuant to the dataset regime is no longer a possibility.
Conclusion
In its annual classified report to the Minister, CSIS stated “When considering the challenges with both the exigent circumstances and normal applications of the dataset regime, it is clear that as currently designed, the regime is incapable of managing the volume and variety of data needed to build a robust and sustainable data analytics program, while maintaining Parliament’s intended control and oversight.”
Having been so involved with the drafting of the regime, CSIS was well positioned to develop policies and procedures governing the collection, evaluation, query, exploitation and verification of datasets. NSIRA expected to find a more mature and compliant application of the dataset regime.
As discussed in this report, CSIS has failed to adequately operationalize the dataset regime. While the regime is indeed complex, CSIS has not sought to clarify legal ambiguities [**redacted**] of the application of the regime before the Court when given the opportunity to do so. Rather, CSIS has adopted multiple positions on the application of the dataset regime that risk limiting what is a collection and retention regime to a retention mechanism. Internally, CSIS has not devoted sufficient resources to ensure compliance to the regime, this extends beyond the compliance incidents noted in this report and includes a lack of dedicated technical experts and systems capable of handling and exploiting bulk data. Nor has CSIS devoted adequate resources to sensitizing its employees to the requirements of the regime through training. Absent appropriate training and internal commitment to adequately resource and support the implementation of a new legal regime, any such regime will fail no matter how fit for purpose it is perceived.
Recommendation 13: NSIRA recommends that CSIS share the full unredacted copy of this report with the Federal Court.
ANNEX A: Technical considerations in the lifecycle of Canadian and foreign datasets
This annex describes the technical processes and systems involved with CSIS’s identification, collection, evaluation, retention, querying, exploitation, ingestion, and destruction of Section 11.01 datasets. CSIS uses similar processes and systems for all Canadian and Foreign datasets. The following description of the technical processes and systems involved with the lifecycle of s.11.01 datasets stems from CSIS briefings delivered on 12 May 2022 and 3 October 2022, a technical demo delivered on 1 November 2022, as well as from the policy suite that governs the collection, evaluation and retention of s.11.01 datasets. This annex should be seen as reflective of the technical processes and systems in place until the end of this report’s review period.
Because datasets are defined by Section 2 of the CSIS Act as “a collection of information stored as an electronic record and characterized by a common subject matter,” the scope and breadth of what may be considered a ‘dataset’ is considerable. Some of the technical challenges that CSIS encounters with datasets stem from the variety of data types [**redacted**], and sizes of files [**redacted**] that can comprise a ‘dataset’.
SIS acknowledges that “while comprehensive, there remains residual risk in these complex systems. They are manual, resource-intensive and subject to error. They reflect the complexity of the datasets regime, and offer limited resilience and scalability.”
Identification and Collection
S.11.01 datasets can be identified and collected by CSIS in a number of ways. For example, Service employees can receive datasets from national and international partners or informants via email, USB drives, external hard drives, or other data storage devices. CSIS employees can [**redacted**], encounter a dataset while performing searches on the internet, [**redacted**]. These diverse processes involve any number of technical processes and systems depending on how, where, and by whom the datasets are identified and collected.
Evaluation
DMEX has centralized the s.11.01 dataset evaluation process; one of DMEX’s designated employees must evaluate the dataset within 90 days of its initial collection. During this 90 day period, a designated employee must determine if the dataset meets the requirements for retention as either a Canadian or foreign dataset. The technical processes and systems involved with the evaluation phase vary depending on the format(s), size(s), and location(s) of the dataset. [**redacted**]. Each dataset must be evaluated using techniques and tools suitable to its unique characteristics. If CSIS initially collected multiple versions of the same dataset, DMEX is responsible for ensuring that all other copies of the dataset have been deleted from Service systems.
If the evaluation results lead DMEX to attempt to retain a Canadian or foreign dataset, CSIS must proceed with the requisite applications for approval and authorization. The systems and programs used to develop materials submitted for approvals and authorizations often lead to the creation of substantial documentation (e.g. memos, briefing notes, and affidavits prepared in Microsoft Word or Excel) describing the datasets. In some cases, copies or subsets of information from the datasets are included in the materials submitted for approval and authorization.
To manage and track a dataset’s evaluation workflow, [**redacted**]. For each dataset it evaluates, DMEX [**redacted**].
Retention and Ingestion
Once a Canadian or foreign dataset has been approved for retention, it is ingested [**redacted**], which is CSIS’s [**redacted**] enables CSIS to store and aggregate all of their operational information and datasets, apply access controls to that information, and perform all requisite security logging processes.
All information ingested into [**redacted**] assigned attribute-based access controls that are mapped to CSIS’s [**redacted**] for designated employees who are evaluating a dataset and [**redacted**] for designated employees who can query and exploit the retained datasets. No other employees can access the datasets.
When employees access datasets, CSIS uses [**redacted**] to collect and index information about what they are doing. CSIS collects [**redacted**].
Querying and Exploitation
[**redacted figure**]
Figure 1: Map of [**redacted**] for querying and exploiting foreign and Canadian datasets.
Only ‘designated employees’ can query and exploit Canadian or foreign datasets, and DMEX has centralized these processes. When a Service employee wants to query a s.11.01 dataset in support of an investigation, they must submit a [**redacted**] to DMEX [**redacted**] . Alongside this request, [**redacted**] The information supplied in each [**redacted**] is used to select the appropriate “justification” when a designated DMEX Analyst performs queries or exploitations [**redacted**] or [**redacted**]. [**redacted**]
If the DMEX analyst finds any results from their queries or exploitations, they record [**redacted**]. They must then contact [**redacted**]. [**redacted**]. This manual set of processes creates multiple copies of raw data from datasets, which can be unintentionally retained on Service employees’ desktop computers or in their email sent/received folders.
[**redacted**] Data is compartmentalized (s.12, s.15, s.16, s.17) based on an investigation’s [**redacted**] and retained as per the [**redacted**] rules associated with it.
[**redacted**] CSIS’s corporate repository. This leads to further duplication of raw data from s.11.01 datasets within CSIS’s digital ecosystem.
Destruction
When datasets are initially ingested into [**redacted**], they are assigned a retention period based on whether they are Canadian or foreign. When that retention period ends, [**redacted**].
ANNEX B: Briefings & Interviews
| Date | Subject |
|---|---|
| Briefings: | |
| February 17, 2021 | Publicly Available Datasets. |
| September 9, 2021 | Foreign Datasets. |
| April 22, 2022 | CSIS Dataset Regime. |
| May 12, 2022 | [**redacted**] Evaluation, Query, Exploitation, Retention & Reporting of Canadian and Foreign Datasets. |
| October 3, 2022 | [**redacted**] |
| November 1, 2022 | Technical Demonstration on Dataset Systems. |
| [**redacted**] | Case Study Briefing. |
| June 6, 2023 | [**redacted**] |
| Interviews: | |
| August 18, 2022 | Canadian dataset. |
| September 6, 2022 | Canadian dataset. |
| October 14, 2022 | Canadian dataset. |
| October 21, 2022 | Canadian dataset. |
ANNEX C: Findings & Recommendations
| Finding 1: NSIRA finds that CSIS’s current application of the dataset regime is inconsistent with the statutory framework. | Recommendation 1: NSIRA recommends that in the next judicial authorization application for a Canadian dataset CSIS put its current position on the application of the dataset regime before the Court, including any use of the information prior to the decision to retain under the dataset regime. |
| Finding 2: NSIRA finds that CSIS’s current approach to dataset information collection under section 12 risks the creation of a parallel collection mechanism, one that weakens section 12’s statutory thresholds and at the same time lacks the external oversight regime intended to protect personal information under the dataset regime. | |
| Finding 3: NSIRA finds that CSIS failed to fully apprise the Court on their interpretation and application of the dataset regime. CSIS should have sought clarification from the Court as to its views on the precise conduct permissible prior to invocating the dataset regime. | |
| Finding 4: NSIRA finds that when conducting queries in exigent circumstances, CSIS retained information that did not meet the section 12 strictly necessary threshold. | Recommendation 2: NSIRA recommends that CSIS immediately destroy any record containing names retained pursuant to the exigent circumstances queries, as they do not meet the strictly necessary threshold. |
| Finding 5: NSIRA finds that the lack of explicit time limits in section 11.17 of the dataset provisions governing foreign datasets has resulted in datasets being retained for multiple years pending a decision by the Minister or Minister’s designate (the CSIS Director). | Recommendation 3: NSIRA recommends that Parliament legislates a time limitation for the authorization of a foreign dataset by the Minister or Minister’s designate. |
| Finding 6: NSIRA finds that CSIS runs the risk of collecting information that is publicly available but for which there may be a reasonable expectation of privacy. | Recommendation 4: NSIRA recommends that CSIS meaningfully analyze and document any possible reasonable expectation of privacy when evaluating publicly available datasets. |
| Finding 7: NSIRA finds that CSIS’s policies governing the collection and retention of Canadian and foreign datasets do not align with its current interpretation of the dataset regime. | Recommendation 5: NSIRA recommends that CSIS develop:
|
| Finding 8: NSIRA finds that CSIS does not have a policy governing the handling of transitory information. In addition, the existing Interim Direction on [**redacted**] does not provide employees with sufficient instruction, which may result in CSIS retaining information that would otherwise be subject to the dataset regime. | |
| Finding 9: NSIRA finds that CSIS information management practices are responsible for multiple compliance incidents and currently create duplicates of datasets within CSIS’s systems. | Recommendation 6: NSIRA recommends that CSIS cease to create duplicates of the information reported in the operational system. |
| Finding 10: NSIRA finds that, as of August 2023, CSIS did not comply with the dataset provisions in the CSIS Act because it retained Canadian information extracted from foreign datasets, and foreign information amounting to a dataset. | Recommendation 7: NSIRA recommends that CSIS immediately destroy Canadian and foreign dataset information that is not strictly necessary to retain. This information no longer falls within the legal 90 day evaluation period and retaining it pursuant to the dataset regime is no longer a possibility. |
| Finding 11: NSIRA finds that CSIS did not comply with the dataset provisions in the CSIS Act because it retained Canadian information and referenced it as recently as 2022. This information should have been destroyed upon coming into force of the NSA 2017, in July, 2019. | |
| Finding 12: NSIRA finds that CSIS has not exhaustively scanned all of its systems to identify information that is subject to the dataset regime so that it may be processed in a compliant manner. | Recommendation 8: NSIRA recommends that CSIS conduct an exhaustive scan of its operational and corporate repositories to identify and destroy any non-compliant information. |
| Finding 13: NSIRA finds that the training required to become a designated employee to evaluate, query, and exploit section 11.01 datasets offers clear information on the collection and retention requirements. | Recommendation 9: NSIRA recommends that CSIS develop and deliver scenario-based workshops to train operational personnel on CSIS’s current application of the dataset regime so that they can engage subject matter experts as necessary. |
| Finding 14: NSIRA finds that CSIS operational personnel, including those predominantly dealing with bulk information collection, have not received adequate training allowing them to identify when collected information may fall within the dataset regime. | |
| Finding 15: NSIRA finds that CSIS has not prioritized resourcing the technical unit responsible for the evaluation, querying, and exploitation of Canadian and foreign datasets. | Recommendation 10: NSIRA recommends that CSIS prioritize resourcing the technical unit responsible for the evaluation, querying, and exploitation of Canadian and foreign datasets. |
| Finding 16: NSIRA finds that CSIS has not devoted sufficient resources to improving the current technical systems or developing new ones that are equipped to support bulk data use. | Recommendation 11: NSIRA recommends that CSIS prioritize the improvement of current technical systems or development of new systems, equipped to support compliant bulk data use. |
| Finding 17: NSIRA finds that CSIS collected information in relation to activities that could not on reasonable grounds be suspected to have constituted a threat to the security of Canada and the collection, analysis, and retention of which was not strictly necessary. | Recommendation 12: NSIRA recommends that CSIS immediately destroy the case study dataset it collected pursuant to section 12, as it does not meet the statutory thresholds. This information no longer falls within the legal 90 day evaluation period and retaining it pursuant to the dataset regime is no longer a possibility. |
| Recommendation 13: NSIRA recommends that CSIS share the full unredacted copy of this report with the Federal Court. | |